In the current dynamic landscape, healthcare application development emerges as a significant opportunity within the healthcare app market. This opportunity is propelled by an increased focus on personal health, rapid technological advancements, and a pressing demand for accessible healthcare solutions. With healthcare professionals and patients increasingly embracing mobile health (mHealth) applications, there’s ample opportunity to develop healthcare apps tailored to their specific needs.
This post delves into the promising realm of healthcare application development, analyzing why the market is so attractive. We’ll explore the essential steps involved in creating these transformative tools, considering technical complexities and financial considerations. Drawing from Mind Studios’ extensive experience, we’ll share insights gleaned from developing an app designed to support individuals dealing with chronic illnesses and injuries.
Development In The Healthcare Mobile App Market
Digitalization has significantly impacted various aspects of our lives, healthcare included. Presently, tasks like scheduling medical appointments, accessing blood test results, and engaging in mental health therapy sessions can all be facilitated through mobile applications. The magnitude of the healthcare app market is noteworthy. App developers are instrumental in guiding clients through crafting a strategic app business blueprint, smoothing the journey from initial concept to market triumph.
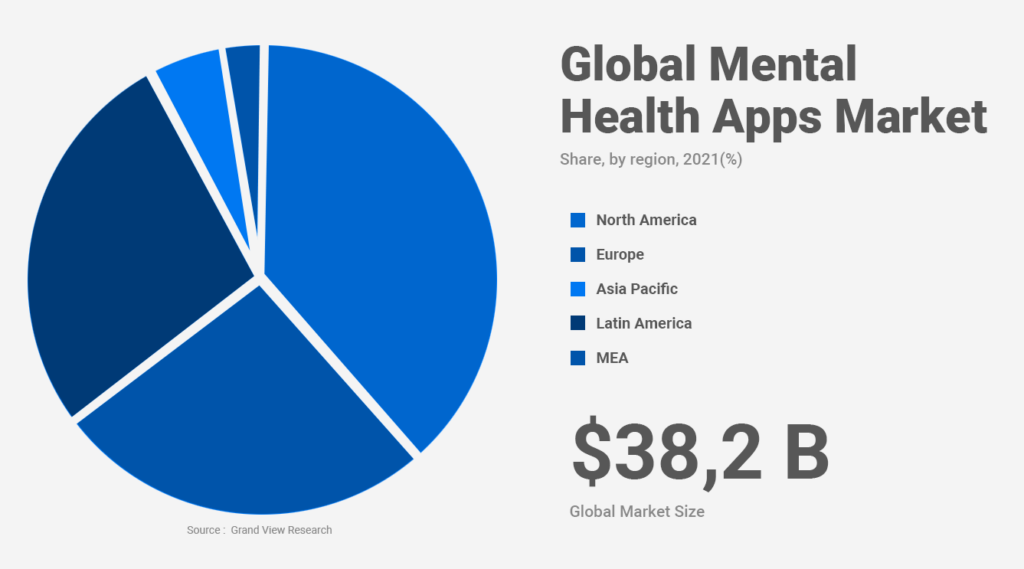
According to a report from Grand View Research, the global mHealth apps market reached a value of USD 38.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8% from 2022 to 2030. North America emerges as the dominant force in this market, claiming 38.2% of the revenue share in 2021.
Moreover, as highlighted in a report by IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science, the abundance of digital health applications available in app stores exceeds 350,000, encompassing both medical and general wellness and fitness apps.
Several factors contribute to the expansion of the healthcare app market:
- Rapid Increase in Smartphone and Internet Users: With smartphones and the Internet becoming ubiquitous, integrating healthcare apps into daily routines has become much easier. This facilitates accessing medical assistance as simply as checking one’s phone.
- Prevalence of Chronic Illnesses Requiring Ongoing Care: Many individuals have chronic health conditions. Consequently, there’s a growing demand for apps that aid individuals in monitoring their health, managing their ailments, and accessing support whenever necessary.
- Advocacy for mHealth Applications by Governmental Bodies and Healthcare Professionals: Governments and healthcare professionals, particularly in regions like the US, are increasingly endorsing mobile apps for health-related purposes. This endorsement encourages broader adoption, ultimately enhancing healthcare accessibility and quality.
- Growing Recognition of the Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: People progressively acknowledge the significance of maintaining good health as a preventive measure. This awareness has led to the increased popularity of wellness-focused apps. Such applications empower individuals to manage their health and well-being actively, addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Furthermore, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred the development of new digital medical tools, including healthcare mobile applications. Therefore, venturing into healthcare app development with the right team increases the likelihood of success.
Difference Between A Health App And A Medical App
Health apps and medical apps are sometimes used interchangeably; however, there is a significant difference between the two.
Health apps are mobile platforms designed to promote general well-being, fitness, and healthy lifestyle choices. They help users track and manage various aspects of their health, such as physical activity, nutrition, sleep, and mental well-being. Examples include MyFitnessPal, Headspace, and Strava, which focus on encouraging healthy habits and providing insights into overall wellness.
In contrast, medical apps have a direct connection to medicine and healthcare. They provide specific medical information and tools for diagnosis, treatment, or managing health conditions. Medical apps must comply with legal data privacy and security regulations and adhere to medical guidelines. Examples include Medscape and Epocrates, offering services like symptom checkers, medication management, telemedicine platforms, and medical reference resources.
Also Read: Angular vs React – Which Framework is the Best for your Application in 2024?
Types Of Healthcare Apps
Depending on the services provided, users must select the app type that best meets their requirements. The following describes the six most frequent types of healthcare apps on the market.

Urgent Care Apps
Emergency Response (ER) platforms, also known as urgent care apps, play a critical role in aiding individuals during emergency situations by providing accessible assistance. These applications are specifically designed to guide people in need towards the appropriate help they require.
Primarily, they offer comprehensive directions to the nearest emergency departments, catering to both insured and uninsured individuals. Additionally, they provide valuable information such as travel routes and estimated waiting times, ensuring that individuals can reach medical assistance promptly.
Key features commonly found in urgent care apps include:
- GPS tracking functionality: This feature enables users to pinpoint their location and locate nearby emergency departments accurately.
- Cost estimation tools: Users can utilize these tools to get an estimate of the expenses associated with seeking emergency medical care, helping them make informed decisions.
- Directory of emergency department contacts: These apps maintain a database of emergency department contacts, making it easier for users to reach out for assistance when needed.
- Emergency contact storage: Users can store contact details of close family members or trusted individuals within the app, facilitating quick communication during emergencies.
Moreover, urgent care apps often provide basic instructions to bystanders, empowering them to offer primary medical assistance to those in need. For instance, these apps may guide in administering aid during situations such as seizures or cardiac emergencies.
Examples of popular urgent care apps include Walk-In Urgent Care and GoHealth Urgent Care, which exemplify the effectiveness and accessibility of such platforms in providing timely assistance during emergencies.
General Hospital Apps
Healthcare apps operated by general hospitals play a crucial role in improving communication with patients and promoting the hospital’s services. These apps streamline various aspects of patient care and management.
Key features essential for general hospital apps include:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Integration: This feature enables seamless access to patient health records, ensuring healthcare providers have up-to-date information on medical history, medications, and treatment plans.
- Doctors’ Profiles and Availability: Patients can view detailed profiles of hospital doctors, including specialties, qualifications, and appointment availability, aiding informed decision-making.
- Patients’ Profiles: Through personal profiles, patients securely access lab reports, test results, and electronic prescriptions, enhancing engagement and empowering them in their healthcare journey.
- List of Treatments and Services: Comprehensive information about medical treatments, procedures, and services helps patients understand available healthcare options.
- Emergency Room Waiting Time: Real-time updates on waiting times assist patients in planning visits effectively, reducing unnecessary wait times and enhancing satisfaction.
Additionally, some hospital apps focus on appointment management, offering functionalities like:
- Appointment Scheduling: Patients can schedule, reschedule, or cancel appointments directly through the app, streamlining the booking process.
- Calendar Integration: Integrated calendars allow both patients and healthcare professionals to manage upcoming appointments and procedures conveniently.
- Virtual Appointments: Hospital apps now offer virtual appointment options via audio or video calls, enabling remote consultations and reducing the need for in-person visits, especially post-pandemic.
Developing hospital apps requires collaboration with medical facilities to ensure they meet the unique needs and challenges of healthcare environments.
Successful examples of hospital apps include Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic Express Care, which effectively leverage technology to enhance patient care and communication.
Diagnostic And Preventive Care Apps
Diagnostic applications primarily serve the purpose of supporting diagnostic medicine by providing patients with convenient access to their personal medical records and test results. Additionally, they facilitate the scheduling of new medical tests. Notably, these applications incorporate symptom checkers to assist patients in identifying necessary tests and appropriate healthcare professionals.
Standard features of diagnostic apps typically include:
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Seamless access to a patient’s medical history and current health information, streamlining the diagnostic process for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Medical Test Scheduling, Costs, and Lab Results: Users can schedule appointments for medical tests, view associated costs, and easily access lab results once available.
- Symptom Checker or AI-Powered Diagnosis Assistant: Advanced algorithms enable users to input symptoms and receive potential diagnoses or recommendations for further testing or consultation.
- Appointment Management: Users can efficiently manage healthcare appointments, including scheduling, rescheduling, and receiving reminders for upcoming appointments.
- Guides and Useful Information: Educational resources and guides on managing chronic illnesses and adopting healthy lifestyle practices empower users to proactively improve their health and well-being.
Examples of well-known diagnostic apps include Symptomate and WebMD, which offer comprehensive functionalities to support patients in managing their healthcare effectively.
Telemedicine Apps
Doctor-on-demand apps, often referred to as telemedicine platforms, offer innovative solutions for accessing healthcare services remotely. These platforms facilitate communication between healthcare professionals and patients through various digital channels such as text, audio, or video, eliminating the need for in-person visits to traditional medical facilities.
The core functionalities of telemedicine apps encompass a range of features designed to streamline the remote healthcare experience:
- EHR Integration: Apps seamlessly connect with electronic health records, aiding efficient access to medical data like histories and prescriptions.
- Patient Profiles: Users create profiles detailing medical history and preferences. Dashboards manage appointments, view results, and track health progress.
- Doctor Profiles: Platforms feature detailed profiles of healthcare professionals, including ratings and reviews for informed decision-making.
- Appointment Management: Convenient scheduling and reminders ensure timely consultations, optimizing patient-doctor interactions.
- Communication Channels: Real-time chats via text, audio, or video accommodate diverse patient needs and preferences.
- E-Prescriptions: Doctors electronically prescribe medications, enhancing patient convenience and efficiency.
- Secure Payments: Integrated payment gateways enable secure transactions for consultations, prescriptions, and services within the app.
Furthermore, telemedicine apps can leverage Internet-of-Things (IoT) technologies to enhance the remote healthcare experience. Patients can use compatible IoT devices to monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, blood sugar levels, or heart rate. Data collected from these devices can be transmitted to healthcare providers in real time, enabling them to make more informed treatment decisions and provide personalized care.
Examples of popular telemedicine apps include MDLIVE, Teladoc, Amwell, and LiveHealth.
Also Read: 15 Game-Changing Mobile App Development Trends In 2024
Healthy Lifestyle Apps
Numerous subcategories fall under the umbrella of this particular type of application. These mobile platforms serve as tools for monitoring various aspects of health and wellness, including but not limited to water and calorie intake, daily step count, and sleep quality assessment. Moreover, some applications extend their utility by offering reminders for users to schedule regular medical checkups, thereby promoting proactive healthcare management.
While the specific features of each app may vary based on their intended purpose, there are several common functionalities that users can expect:
- User Profiles: Within the app, users have the option to create personalized profiles, inputting data like activity level, weight, and medical history. This data forms the basis for customizing app recommendations and monitoring progress over time.
- Habit Tracking: These apps often feature tools for monitoring daily habits related to nutrition, exercise, and overall wellness. Users can log meals, track workouts, and monitor sleep patterns to stay on track with their health objectives.
- Push Notifications: Utilizing push notifications, these applications offer timely reminders and motivation to keep users engaged and accountable. Notifications prompt users to log activities, remind them of goals, and provide encouragement along their health journey.
- Guidance and Resources: Many apps provide valuable resources including nutritional guides, workout plans, and wellness advice. By offering accessible guidance, users can make informed decisions regarding their health and lifestyle.
Examples of such applications that encompass these features include Sleep Cycle, Plant Nanny, and Better Me. Each of these apps aims to empower users to take control of their health and well-being through proactive monitoring, personalized guidance, and positive reinforcement.
Mental Health Apps
Mental health apps play a vital role in assisting individuals in effectively managing a spectrum of mental health conditions, encompassing anxiety, depression, and eating disorders. Their primary objective is to equip patients with an array of tools aimed at facilitating the monitoring and enhancement of their progress along the path to mental well-being.
These apps typically incorporate the following key features:
- Communication Channels: Users can engage with licensed therapists via text, audio, or video chat, ensuring seamless access to professional support.
- Therapy Session Management: Our apps feature intuitive scheduling systems, enabling users to arrange therapy sessions conveniently and ensuring timely access to care.
- Progress Tracking Tools: Integrated comprehensive trackers allow users to monitor their mental health progress, empowering informed decision-making and goal-setting.
- Mental Health Enhancement Activities: We offer diverse activities like meditation, relaxation techniques, and cognitive exercises to enhance mental well-being.
- Supportive Community Engagement: Our apps foster peer-to-peer interaction through support group chat features, creating a supportive environment for shared experiences and encouragement.
- Access to Medical Records: Users can securely access and manage their medical records, empowering them to take an active role in their healthcare journey.
Examples of prominent mental health apps embodying these features include VOS, Headspace, and Talkspace. Through their comprehensive offerings, these platforms aim to democratize access to mental health support and empower individuals to proactively prioritize their well-being.
Essential Features Of A Healthcare App Worth Utilizing
The features of a healthcare app vary depending on its type and primary function. Nonetheless, several features are essential for most mHealth apps, including telemedicine, general hospital, or urgent care apps. Here’s a list of these crucial features:
| Feature | Description |
| Sign-up / Sign-in | Quick and seamless sign-in process, possibly via email client. |
| Doctors’ Profiles | Contains specialization, education details, workplace, availability, etc. |
| Patients’ Profiles | Contains medical information like medication, medical history, etc. |
| Appointment Management | Allows doctors to view appointments and patients to check doctors’ availability and book appointments. |
| In-app Chat | Enables quick communication with healthcare facility managers or doctors. |
| Video Consultations | Facilitates online consultations via video calls, reducing time and health risks associated with in-person visits. |
| EHR Integration | Integrates electronic health records (EHR) for maintaining patients’ treatment history and aiding future care. |
| E-prescriptions | Enables online prescription of medication, enhancing security and convenience. |
| Payment Gateway | Supports various payment methods including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, crypto payments, etc. |
| Ratings and Reviews | Allows patients to evaluate professionals and make informed choices. |
| Push Notifications | Sends reminders for upcoming consultations and medication alarms to both healthcare workers and patients. |
Also Read: 7 Frameworks for Cross Platform Mobile App development
Optimal Technological Framework For Developing Mobile Apps In Healthcare
Discussing the tech stack is crucial when addressing the fundamental question of developing a health app.
The selection of technology for creating a health app significantly impacts its future performance and user convenience. Below is an outline of the technology stack for your medical application development should you opt to proceed.
| Feature | Technology |
| Sign-up / Sign-in | Facebook API, Google API |
| Chat | Twilio |
| Audio / Video Calls | WebRTC, RTMP |
| EHR | REST API, GraphQL |
| Payment Functionality | Stripe, PayPal |
| Calendar | Google Calendar API |
| Notifications | Firebase SDK, APNs |
| Storage | Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage |
| Backend | Ruby on Rails, Elixir/Phoenix, Node.js |
| Database | MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB |
| Web App | JavaScript, HTML, CSS, Vue.js, React.js |
| iOS App | Swift |
| Android App | Kotlin, Java |
Key Factors to Evaluate Before Developing a Healthcare Mobile Application
Moreover, apart from the features and technology selection, several other aspects of healthcare app development warrant consideration. Below, we outline a list of the most critical ones.

Mobile Platform Choice
In mobile app development, it’s common practice to begin with one platform, like iOS or Android, then expand as needed. This strategy is logical, especially for health-focused apps like habit trackers or meditation platforms, particularly in the early stages of creating a minimum viable product (MVP).
However, when creating apps for hospitals, it’s recommended to release both iOS and Android versions simultaneously. The primary aim for healthcare providers, including general hospitals, transitioning to digital platforms is to improve healthcare accessibility, a goal hindered if one patient segment is favored over another.
Interoperability
Developing a healthcare app, especially one centered on medical services, requires smooth integration with various medical systems and databases used by healthcare providers. The level of interoperability directly impacts the compatibility between the app and these medical systems.
Healthcare interoperability, defined by IBM, involves the efficient and secure exchange, integration, and utilization of electronic health records to improve health outcomes for individuals and communities.
In essence, creating a health app with a high level of interoperability simplifies the delivery of medical services for healthcare professionals. This encompasses tasks such as accessing patients’ electronic health records, ordering tests, and reviewing results, ultimately enhancing the quality and efficiency of medical care.
Therefore, if you’re developing a medical app for both healthcare professionals and patients, ensure seamless integration of all health systems within your app to function as a unified ecosystem. To achieve this, leveraging APIs like SMART is essential, as it enables the development of interoperable solutions synchronized with digital medical systems.
IoT Integration
Daily monitoring of steps taken, vital signs, and stress levels relies on using additional devices such as smartwatches and various healthcare tools. These devices can seamlessly synchronize with the respective applications by incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) technology.
In healthcare software, the integration of IoT serves a crucial purpose: enabling remote patient monitoring. This means doctors and patients can effectively track important health indicators such as glucose levels and heart rate. Moreover, IoT facilitates the continuous observation of a patient’s mental health, including the progression of depression symptoms.
A compelling example of IoT’s efficacy lies in its application for individuals grappling with Parkinson’s disease. Comprehensive data on symptomatology can be collected through IoT sensors strategically placed in their environment. This data empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about treatment plans and adjustments, ultimately enhancing patient care and quality of life.
Proper Security
Securing user data is the primary focus in developing healthcare software tailored to user needs. Besides facilitating the exchange of sensitive medical information, your application may handle financial transactions, highlighting the importance of establishing trust with your clientele through a highly secure healthcare app.
To strengthen defenses against potential data breaches and fraudulent activities, it’s essential to implement robust measures such as end-to-end data encryption and multifactor authentication protocols. These safeguards enhance the application’s security and increase user confidence in its reliability and integrity.
Moreover, understanding the diverse legal frameworks governing personal data protection across different countries, especially concerning patient data, is crucial. Developers entering healthcare application development must grasp and adhere to relevant regulatory frameworks to ensure legal compliance and user trust.
Ensuring Compliance With Health App Regulations
Developing a medical application, whether for an emergency room or a general hospital platform, involves numerous responsibilities, particularly navigating legal and safety regulations, especially concerning sensitive user data.
We’ve compiled a comprehensive list of regulations your application may need to follow, depending on the geographic regions you target. Complying with these frameworks ensures adherence to app store guidelines and guards against potential legal issues.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The GDPR is a cornerstone of EU law regarding data protection and privacy within the European Union and the European Economic Area. Globally recognized for its strict approach, it covers various data types, including patient health records.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA, a US federal law, is meticulously designed to protect sensitive patient health information from unauthorized disclosure. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for apps targeting the US market.
PIPEDA (The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act)
PIPEDA is Canada’s primary privacy law governing the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data by private entities. Particularly relevant to medical records, it mandates obtaining individuals’ consent before collecting, using, or disclosing their information.
DPA (Data Protection Act)
The DPA in the UK governs the acquisition and processing of personal data, emphasizing individuals’ rights to access their personal information.
While these regulations provide a fundamental framework, it’s important to note some overlap among them. For example, an application compliant with HIPAA in the USA automatically adheres to HiTECH, another US regulation addressing EHR data security. Similarly, parallels can be drawn between Canada’s PIPEDA and Europe’s GDPR, reflecting shared objectives in privacy protection.
Healthcare Application Development Steps
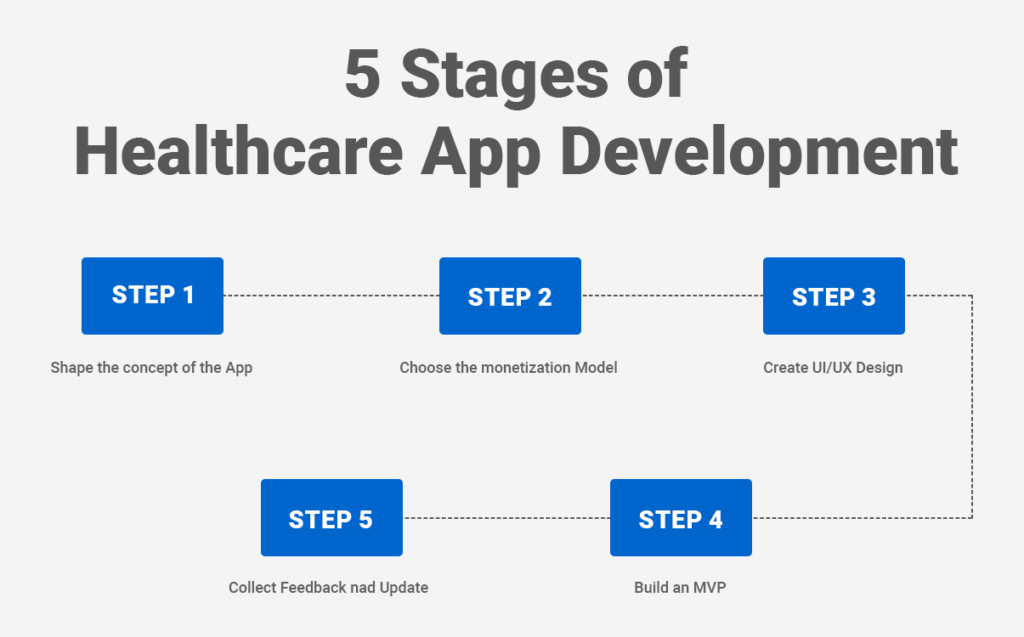
Developing a healthcare application involves five essential stages that are indispensable for understanding the process:
Step 1: Conceptualize the app’s idea.
Step 2: Select a monetization model.
Step 3: Design the UI/UX.
Step 4: Develop a Minimum Viable Product (MVP).
Step 5: Gather feedback and implement updates.
Step 1: Conceptualize The App’s Idea
When embarking on healthcare app development, addressing the core question is paramount: What motivates users to download and continue using your app? Undertake strategic steps to answer this effectively:
- Define prospective users: Delve beyond demographics to understand lifestyles, preferences, and pain points, tailoring the app accordingly.
- Conduct market research: Analyze the competitive landscape to identify opportunities and gaps, positioning the app effectively.
- Identify selling points: Compile unique features, user experience enhancements, or additional services resonating with the target audience.
- Define app goals and budget: Clearly articulate objectives aligned with available resources to measure success against predefined metrics.
Following these steps ensures a comprehensive understanding, aiding in the development of a standout healthcare app.
Step 2: Select A Monetization Model
Healthcare providers considering the development of a healthcare app often prioritize its utility over direct monetization, viewing it as a supplementary tool to enhance their services. Conversely, for apps focused on promoting meditation or a healthy lifestyle, the monetization strategy requires a more nuanced approach. The four primary monetization models are as follows:
- Freemium model: The app is free to use, but certain features require in-app purchases.
- Subscription model: Users gain access to all or select features through a subscription, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis.
- In-app ads: The app is free, but user sessions may be interrupted by banners, videos, or other forms of advertisements.
- Paid apps: Users must purchase the app directly from the app store before downloading it. However, this approach is more suitable for established businesses.
Owners have the flexibility to choose a single monetization model or combine several approaches to align with their goals.
Step 3: Design The UI/UX
During the outlined stage, UI/UX designers engage in a thorough process to define both the functionality and visual aesthetics of the application. This involves meticulous planning and execution to ensure the app performs its intended tasks and resonates with users visually. Additionally, designers delve into the branding aspect of the platform, aligning it with overarching themes and corporate identity guidelines.
A significant part of this phase revolves around creating prototypes—detailed visual mockups illustrating each screen of the application and user interactions. These prototypes act as blueprints for the development team, offering a clear roadmap for implementation while enabling stakeholders to visualize the final product.
Attention to detail is crucial, with every element meticulously considered, from font choice to button placement, enhancing usability and attractiveness. For mHealth platforms, ensuring responsiveness across all devices is paramount for accessibility and usability. Designers prioritize simplifying the user journey, streamlining navigation, and prioritizing key features to exceed user expectations and contribute to platform success.
Step 4: Develop A Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Healthcare mobile app development projects often involve a high level of technological complexity, leading to significant costs. However, limited funding shouldn’t impede progress.
An MVP (minimum viable product) allows for the initial implementation of essential features to fulfill the primary app objectives. This approach facilitates quicker user feedback collection and provides an opportunity to secure additional funding for further development.
Choosing an MVP helps mitigate financial risks by providing a cost-effective means of assessing product viability before making extensive investments. While our team generally advocates for an MLP (minimum lovable product) in initial releases, we recognize the importance of tailoring our approach to individual project requirements.
To delve deeper into these options, examine their distinctions, and determine the most suitable fit for your needs and resources.
Step 5: Gather Feedback And Implement Updates
Whether you opt for launching with an MVP or an MLP, it’s crucial to address user feedback and update the app promptly. After developers deploy the updates, QA engineers conduct thorough testing to ensure there are no bugs and that the project requirements align with the outcomes.
How Much Does It Cost To Build A Healthcare App
The cost of your future app is primarily influenced by two factors: the complexity of the platform and the choice of the development team.
To incorporate all essential mHealth features, you’ll require a team comprising:
- 1 project manager
- 1 product manager or business analyst
- 1 UI/UX designer
- 1 iOS developer
- 1 Android developer
- 1 backend developer
- 1 QA engineer
Regarding development team options, you can opt for an in-house team or hire an outsourced team. The latter tends to be less expensive as you can select a skilled team from any part of the world within your budget. For example, developers from Eastern Europe typically charge about three times less than their US counterparts while delivering comparable results.
As you are aware, there are various types of healthcare apps. Here, we’ve provided an estimate for building a medical app allowing patients to schedule appointments and have video consultations with doctors. The estimate is based on an average Eastern European rate of $45/hour.
| Stage | Time (hours) | Cost (USD) |
| Discovery stage | 80+ | 3,600 |
| UI/UX design | 220 | 9,900 |
| iOS development | 790 | 35,550 |
| Android development | 810 | 36,450 |
| Backend development | 680 | 30,600 |
| Testing | 380 | 15,200 |
| Project management | 360 | 14,400 |
| Total | 3,320 | 145,700 |
It’s important to remember that even after the app is launched, ongoing funding will be necessary for maintenance, regular updates, and marketing efforts.
Selecting A Healthcare App Development Team
Partnering with a skilled and trustworthy healthcare app development team is a critical decision that significantly impacts the success and effectiveness of your project. To ensure you make the right choice, it’s essential to follow a thorough process:
Step 1: Identify Your Requirements
Start by precisely defining the goals and unique needs of your project. This entails comprehending the fundamental objectives you strive to accomplish and the features your application should provide. By establishing a precise vision for your project, you can effectively assess the suitable development team. Evaluate aspects like their industry experience, proficiency in healthcare technology, adherence to regulatory norms, and pricing models.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Explore reputable platforms like Clutch and GoodFirms to identify potential development teams. These platforms allow you to set criteria based on your preferences, such as budget, location, and industry expertise. Take time to read reviews and assess the quality of work showcased in their portfolios. Prioritize companies with a proven track record in developing healthcare apps or similar projects.
Additionally, leverage your professional network to gather referrals and recommendations from colleagues or industry peers who have firsthand experience working with development teams.
Step 3: Make A Shortlist And Conduct Interviews
Based on your research, compile a shortlist of promising candidates. Arrange interviews to delve deeper into their capabilities, work process, and cultural fit with your organization. During these discussions, clarify your project requirements and gauge their understanding and enthusiasm for the task at hand.
If possible, involve your internal IT team in technical interviews to assess the developers’ proficiency and compatibility with your technology stack. Furthermore, reach out to their previous clients to gather insights into their performance and client satisfaction.
Step 4: Negotiate Terms And Finalize The Agreement
Once you’ve identified a suitable development partner, negotiate the terms of engagement to ensure a mutually beneficial arrangement. Discuss important aspects such as communication protocols, project timelines, milestone delivery, change management procedures, intellectual property rights, and ongoing support post-launch.
It’s crucial to establish a clear understanding of expectations and responsibilities to minimize potential conflicts down the line. Draft a comprehensive contract that outlines these agreements and ensures legal protection for both parties.
Healthcare App Development Experience

In the dynamic realm of healthcare app development, despite market saturation, numerous opportunities await exploration. A notable project showcasing this potential is Envol, an extensive endeavor encompassing diverse functionalities aimed at innovation.
Envol integrates features from various app categories like meditation, wellness, performance tracking, and habit formation, targeting support for individuals recovering from chronic ailments and injuries. Originating from personal experiences, particularly Julie’s journey of overcoming illness, Envol embodies a unique methodology supported by empirical medical research.
The transition to Envol posed challenges, including migrating existing users seamlessly to the new platform without compromising data integrity. Despite manual data migration in some cases, the team ensured continuity in user experience, fostering collaboration with creators Julie and Tim throughout development.
Post-launch, ongoing support and iterative enhancements are prioritized, with the team assisting in marketing endeavors to ensure Envol’s success. Committed to its enduring journey, the team remains confident in Envol’s promising prospects.
Conclusion
The digitalization of healthcare benefits both patients and medical professionals, leading to an increasing demand for tools that facilitate their connection. Furthermore, developing healthcare apps presents an opportunity to enhance preventive care, potentially benefiting the global population in the long term.
This article discusses different types of healthcare apps, including those focused on promoting healthy habits and those designed for medical professionals. If you require guidance on creating a healthcare app tailored to your needs, our business development team is available to arrange a complimentary consultation.
FAQs
What features should a healthcare app include?
A robust healthcare app must encompass key features: appointment scheduling and reminders, EHR management, telemedicine for remote consultations, medication tracking and reminders, health data monitoring, secure patient-provider messaging, integration with wearable devices, emergency assistance, and access to health education resources.
How can I ensure the security and privacy of healthcare data in my app?
Ensuring the security and privacy of healthcare data within the app requires robust measures. This entails implementing end-to-end encryption for data transmission, securely storing sensitive information with encryption and access controls, and adhering to healthcare data protection regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Regularly updating the app to address security vulnerabilities and conducting security audits and penetration testing are crucial steps.
Additionally, educating users about data security best practices can further bolster security measures.
What technologies should I consider for developing a healthcare app?
Developing a healthcare app involves choosing from diverse technologies. Options include mobile app frameworks like React Native, Flutter, or native development for iOS and Android. Backend technologies like Node.js, Django, or Flask enable robust API construction. Scalable infrastructure can be built using cloud computing platforms like AWS or Google Cloud. Database technologies like MongoDB or PostgreSQL provide secure data storage solutions. Integrating APIs for telemedicine, EHR systems, and other healthcare services enhances overall functionality.
How do I ensure my healthcare app is compliant with regulations like HIPAA?
Compliance with regulations like HIPAA involves several key steps: understanding requirements, implementing technical safeguards (encryption, access controls), conducting regular risk assessments, training development teams, and collaborating with healthcare compliance experts for thorough reviews.